In the first part of the eFisc-Thurgau guide, we filled in the first three parts of our Swiss tax return (for the canton of Thurgau): personal data, bank details for refunds and income from a professional activity.
Now let’s move on to the other categories, especially the interesting part about real estate!
Step 1: Real estate (owned or leased)
This form is one of the most important. It concerns deductions for income and assets at the same time.
As a tenant
If you are a tenant, you can skip this section and go straight to deductions.
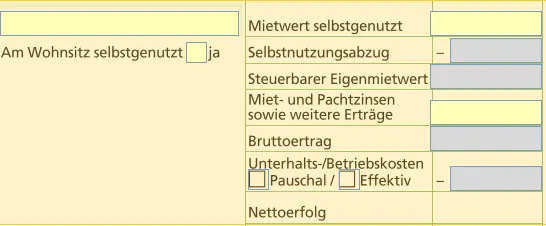
As an owner of your own property
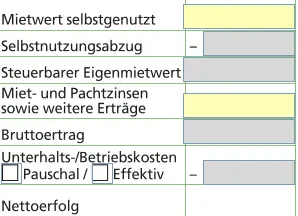
Enter each property separately. For personal use only.
You will obtain the tax and rental values for the canton of Thurgau. These values must be entered exactly.
You can enter maintenance costs:
- make a flat-rate claim
- or make an actual claim with supporting documents
Only costs incurred to maintain the value of the property are deductible (i.e. not costs incurred to improve comfort, such as adding a pergola).
Real estate leased as owner
For rented properties, you enter the rental income instead of the rental value. Here too, you can enter maintenance and operating costs on a flat-rate or actual basis.
Step 2: Professional deductions
Before submitting my tax return, I always go through the same checklist to avoid costly oversights. I detail all my Swiss tax deductions here, with concrete real-life examples:
My Swiss tax deductions: real-life example and checklist (2026)
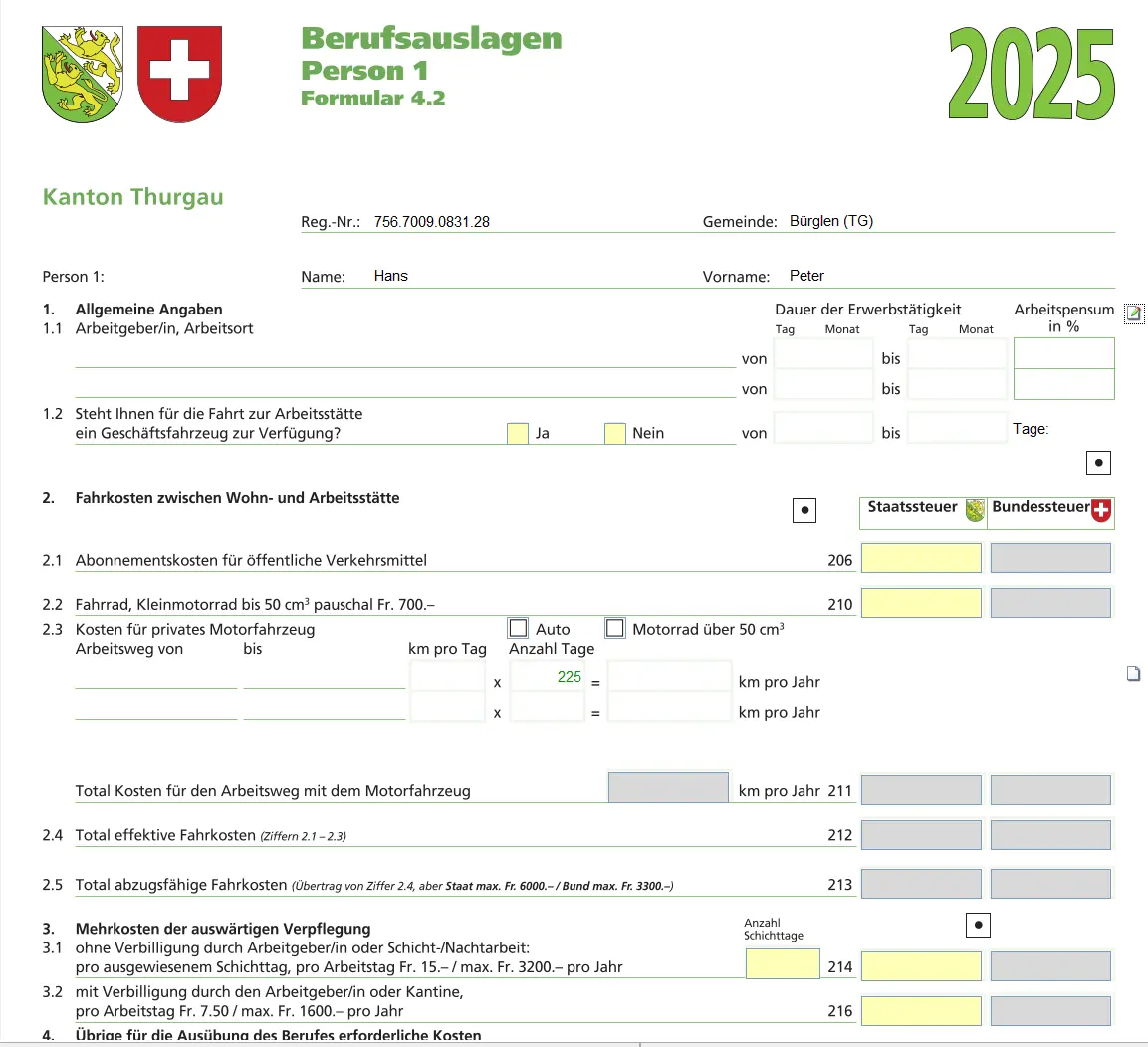
Travel expenses
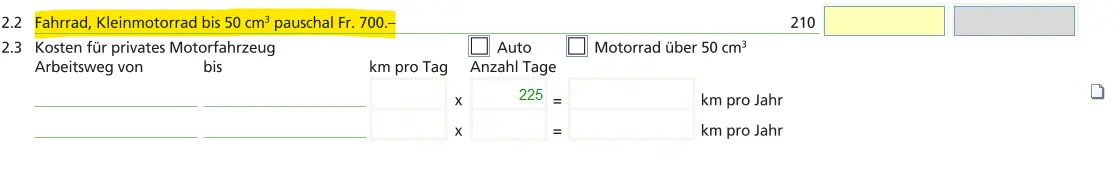
You can deduct commuting expenses, provided you pay them yourself. As a rule, these are public transport costs. A flat-rate deduction for bicycles is also possible.
Car expenses are only admissible under certain conditions (e.g. if you start work early, and there is no public transport at that time).
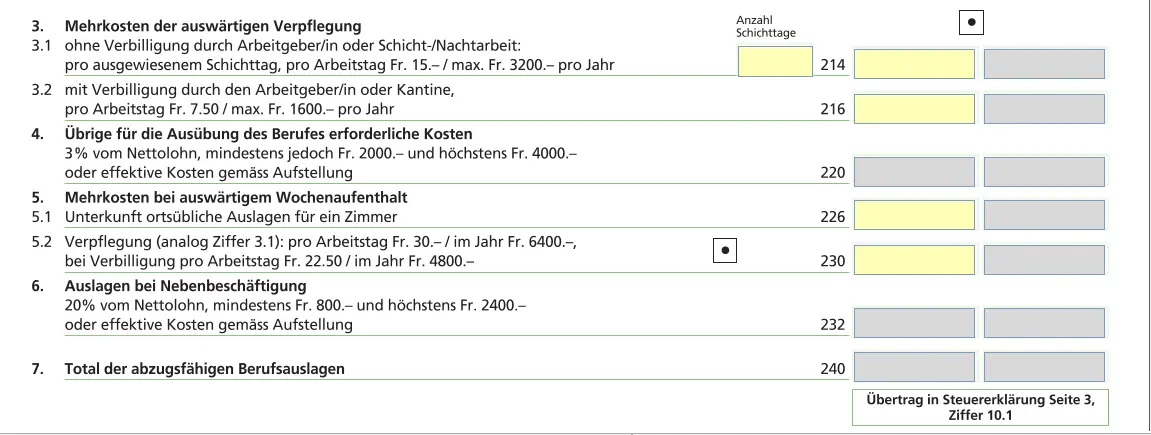
Other business expenses
Here you can claim meal expenses and other business expenses. By default, a flat-rate deduction is granted. Actual expenses are only worthwhile if they are higher and can be justified.
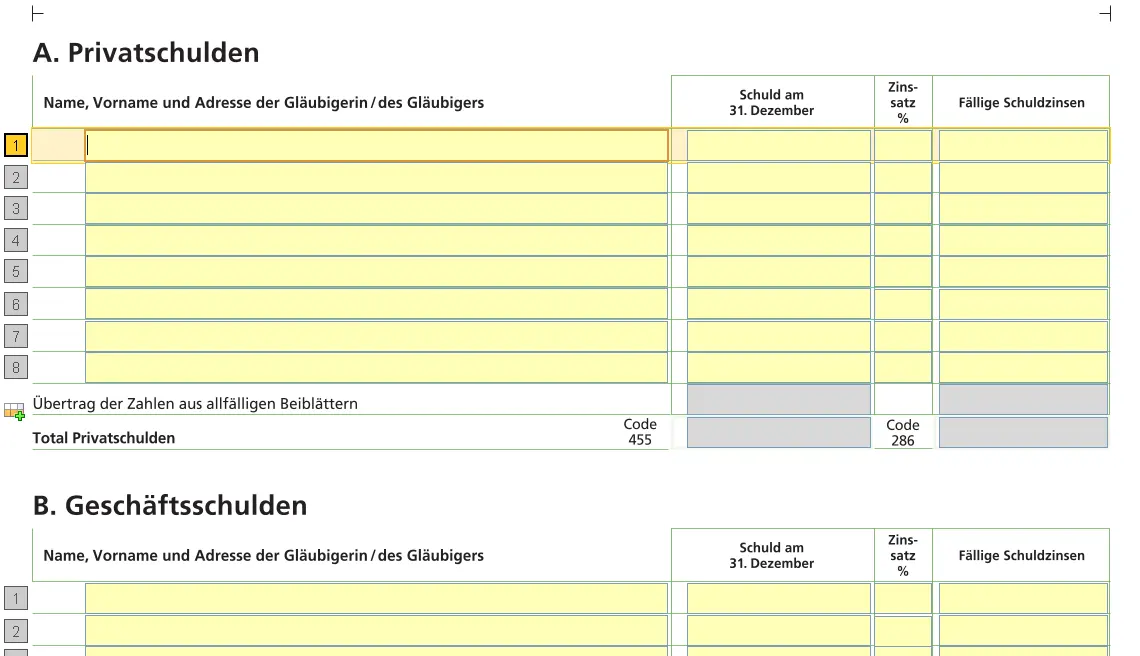
Step 3: Debts
Are deductible
- Mortgages
- Private loans
- Federal taxes due at 31.12
Car leasing is not deductible.
Step 4: Pension and insurance
Pillar 3a and pension provision
You register here:
- Pillar 3a payments (maximum amount 2025 = CHF 7'258 )
- Pension fund purchases
- AHV contributions for non-employed persons
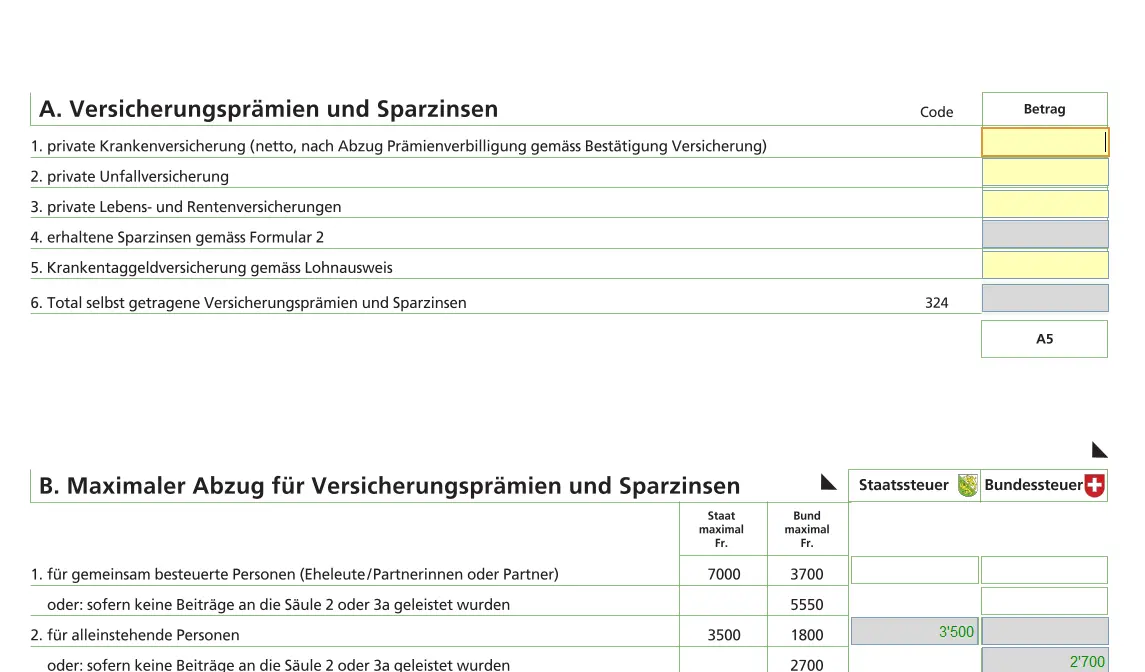
Health insurance premiums
Premiums for you and your family are entered here. Subsidies must also be entered.
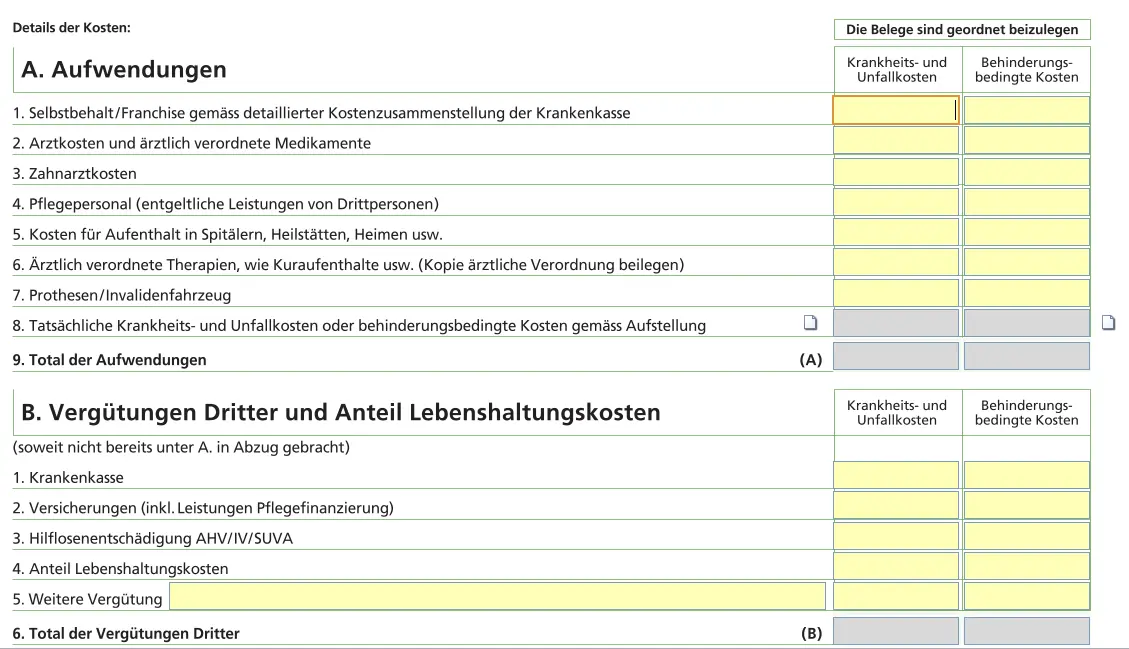
Sickness and accident costs
Expenses that are not covered, such as dental co-payments, glasses or treatment, can be claimed here.
Next step
After all, it’s not that complicated to file your Swiss tax return, is it?
In part 3 of our eFisc-Thurgau tutorial, we’ll cover the following sections:
- Donations
- Bank accounts
- Investment securities
- Electronic tax statement
- Other assets
- Closing
If you find other tax optimization possibilities in the screenshots above (or if you have a question), don’t hesitate to send them to me in the comments!